The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, has been one of the most significant global health crises in modern history. It has affected nearly every aspect of life, from healthcare systems to economies, education, and social interactions. Understanding the timeline of the pandemic—when it started, how it evolved, and when it might end—is crucial for comprehending its impact and preparing for future challenges.
The Beginning: When Did the Pandemic Start?
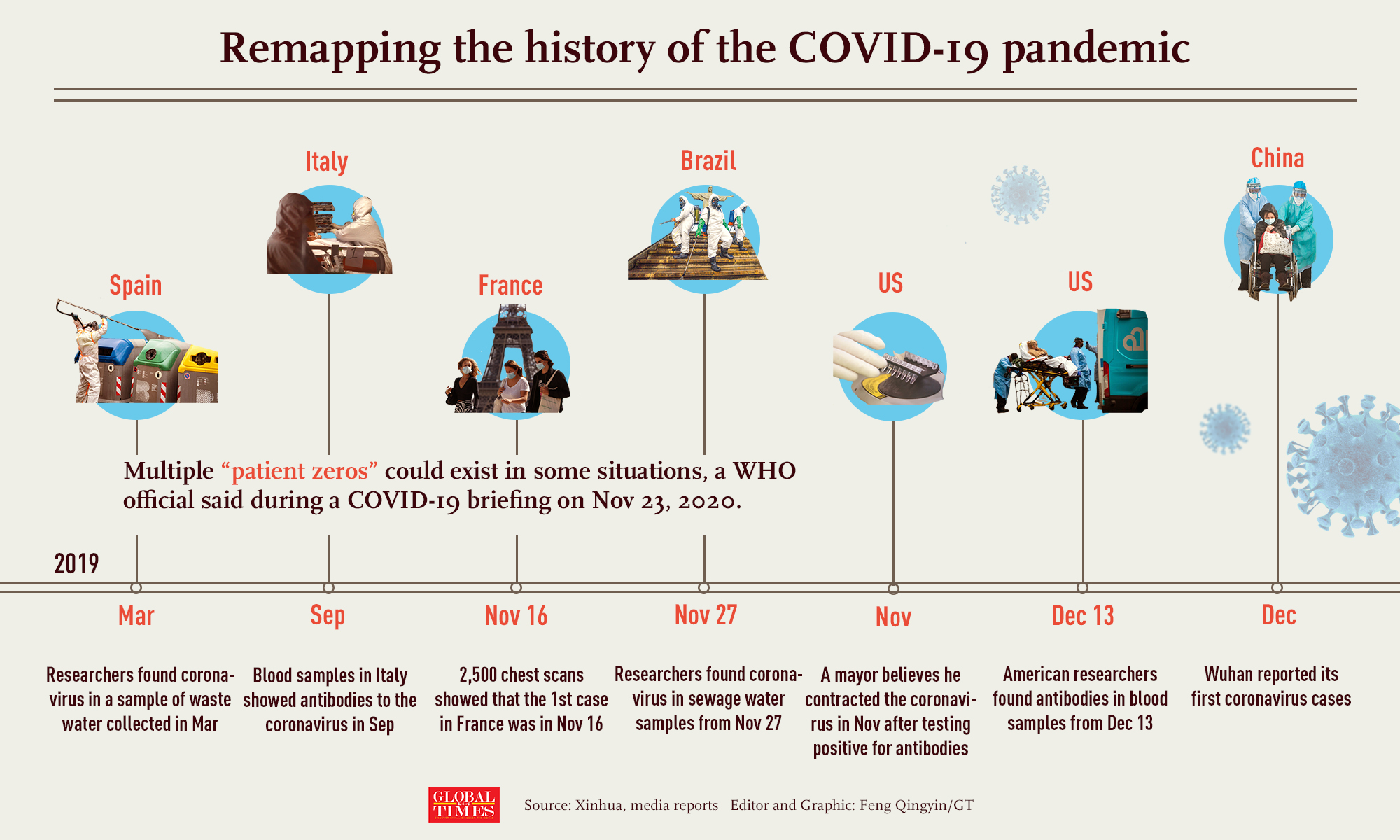
The COVID-19 pandemic officially began inDecember 2019, when a cluster of pneumonia cases of unknown origin was reported in Wuhan, the capital of Hubei Province in China. The initial cases were linked to the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market, where live animals were also sold, suggesting a possible zoonotic origin. OnDecember 31, 2019, the World Health Organization (WHO) was alerted to these cases, and byJanuary 7, 2020, Chinese authorities identified the causative agent as a novel coronavirus, later named SARS-CoV-2.
The first death attributed to COVID-19 occurred onJanuary 11, 2020, in Wuhan. ByJanuary 13, 2020, the virus had spread beyond China, with the first case reported in Thailand. The WHO declared the outbreak a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) onJanuary 30, 2020, and byMarch 11, 2020, it was characterized as a pandemic, marking the global spread of the virus.
The Global Spread and Impact
The rapid spread of COVID-19 was facilitated by international travel and the highly contagious nature of the virus. ByMarch 2020, countries around the world began implementing lockdowns, travel restrictions, and social distancing measures to curb the spread. The pandemic led to unprecedented disruptions in daily life, with schools, businesses, and public spaces closing, and healthcare systems overwhelmed by the surge in cases.
The economic impact was severe, with global GDP contracting by3.5% in 2020, the worst recession since World War II. Unemployment rates soared, and millions of people were pushed into poverty. The pandemic also exposed and exacerbated existing inequalities, with vulnerable populations, including the elderly, those with pre-existing conditions, and marginalized communities, disproportionately affected.

The Development of Vaccines and Treatments
One of the most significant milestones in the fight against COVID-19 was the rapid development of vaccines. The first COVID-19 vaccine, developed by Pfizer-BioNTech, was authorized for emergency use in the United States onDecember 11, 2020, followed by other vaccines such as Moderna, AstraZeneca, and Johnson & Johnson. The global vaccination campaign began in earnest inearly 2021, with countries prioritizing healthcare workers, the elderly, and other high-risk groups.
The development of vaccines was a remarkable scientific achievement, with the process typically taking years compressed into months. However, the rollout faced challenges, including vaccine hesitancy, supply chain issues, and inequitable distribution, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
In addition to vaccines, treatments for COVID-19 were also developed. Antiviral drugs like remdesivir and monoclonal antibodies were authorized for emergency use, and research into other therapies continued. The use of dexamethasone, a corticosteroid, was found to reduce mortality in severe cases.
The Emergence of Variants
As the virus spread, it mutated, leading to the emergence of new variants. Some of these variants, such as Alpha (B.1.1.7), Beta (B.1.351), Gamma (P.1), and Delta (B.1.617.2), were more transmissible and, in some cases, more virulent. The Delta variant, first identified in India inlate 2020, became the dominant strain globally bymid-2021, leading to new waves of infections and hospitalizations.
The most concerning variant to date is Omicron (B.1.1.529), first detected in South Africa inNovember 2021. Omicron is highly transmissible and has a significant ability to evade immunity from previous infection or vaccination, leading to a surge in cases worldwide. However, it appears to cause less severe disease compared to previous variants, particularly in vaccinated individuals.
The Current State: When Will the Pandemic End?
As of2023, the COVID-19 pandemic is not yet over, but the situation has evolved. Many countries have transitioned from a pandemic to an endemic phase, where the virus continues to circulate but at lower, more manageable levels. This shift has been facilitated by high levels of vaccination, natural immunity from previous infections, and improved treatments.
The WHO has emphasized that the end of the pandemic will not be a single event but a gradual process. The focus has shifted from containment to managing the virus as part of everyday life, similar to how we manage influenza. However, the risk of new variants and potential surges remains, particularly in regions with low vaccination rates.
Lessons Learned and Future Preparedness
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of global cooperation, scientific innovation, and public health infrastructure. It has also underscored the need for equitable access to vaccines and treatments, as well as the importance of addressing misinformation and vaccine hesitancy.
Looking ahead, the world must prepare for future pandemics by investing in pandemic preparedness, strengthening healthcare systems, and fostering international collaboration. The lessons learned from COVID-19 will be invaluable in mitigating the impact of future health crises.
The COVID-19 pandemic began inDecember 2019 and has had a profound impact on the world. While the pandemic is not yet over, significant progress has been made in controlling the virus through vaccination, treatments, and public health measures. The transition to an endemic phase is underway, but vigilance and preparedness remain essential. The end of the pandemic will be a gradual process, and the lessons learned will shape our response to future global health challenges.
发表评论
暂时没有评论,来抢沙发吧~